Multi-disciplinary Clinical Skills & Simulation Training Centre
Skill Lab/ Simulation Laboratory
Medical, Surgical, Obstetric and Radiology specialties have progressed in leaps and bounds in the last decade. With the advent of highly technical investigative and therapeutic tools medical, surgical, radiological procedures have become highly specific and precise resulting in reduced morbidity and mortality. The modem doctor provides effective care only by using these tools. Effective training is required before a doctor can use these tools. Among the three major domains of learning for a doctor, Viz. Knowledge, Skills and ethics, knowledge and ethics are learnt and imbibed by various effective teaching/learning methods with existing facilities.
Learning skills & competencies, however, is a major challenge. It is a challenge because
• Opportunities for learning and chances of repeating performances on patients are limited
• Safety of patients during training is a concern
• Patient expectations are high, with a reluctance to let trainees do procedures.
• Refining the skills and acquiring competency on patients directly is a problem.
Hence, it is important to impart basic skills in the laboratory / Training Centre environment and then allow the reasonably trained student to hone his skills further, on a patient. Basic Medical, Surgical Obstetric & Radiological Skills Centre (BSC) would meet this requirement. This need has been realized for many years in western countries. Many countries mandate a formal certificate in Basic Skills before allowing students to take postgraduate examinations.
Beneficiaries:
1. MBBS STUDENTS
2. MD/MS STUDENTS
3. NURSING STUDENTS [Diploma, B.Sc and M.Sc]
4. OT & Anesthesia Technologists
5. PARA MEDICAL COURSE STUDENTS
[Any individual involved in patient care in most of the surgical /critical care will be benefitted.]
Postgraduates need advanced training in surgical skills including Laparoscopic surgical skills; Postgraduates from various surgical disciplines would need a common set medical, surgical, obstetric and radiological skills like clinical examination, dissection techniques, suturing, knot tying, laparoscopic skills, wound management skills, delivery, obstetric examination and maneuvers, Sonography, CT Scan, Lumbar puncture etc.
The term postgraduate would also encompass many ‘medical’ specialties undertaking invasive procedures like insertion of chest drains, pacemakers , liver biopsies etc.This centre functions as nodal centre for training not only our University students but is also planning to include students of other institutes as well in this academic year. With these priorities in mind this centre is proposed.
Goal:
A centre of excellence in learning basic and advanced skills so as to enable health care profession students to be competent in delivering the health care needs effectively to enable health care profession students to be competent in delivering the health care needs effectively.
Objectives:
1. To train and develop necessary clinical skills in medical undergraduate, post graduate students, paramedical students as per needs and competency statements of various courses.
2. To train and certify the learners and faculty necessary for conducting courses or establishing such centers elsewhere
3. To develop and act as a resource center for such activities and co ordinate between various sections for effective delivery.
4. To develop resources, materials and course curricula required for various courses
5. To train and certify the learners and faculty
6. To provide intellectual support for upcoming centers

Programs in skills training and simulation-based education are necessary to avert unnecessary medical errors and to offer quality health care services to people. The establishment of skills laboratory is a step towards achieving the goal of Indian Medical Graduate (IMG) who is a well-trained skilful professional.
In other words, the simulation and training solutions will enable the learners and provide opportunity for hands-on deliberate practice, development of decision-making skills, and improved communication and teamwork.
SKILLS TRAINING CENTRE:
The skills development centres will consist of:
• A simulation laboratory for developing basic clinical, procedural and surgical skills.
• A laparoscopic training facility for acquiring basic skills in laparoscopy
• The facility will be also to open to undergraduate and postgraduate students, interns and residents, who can come for skills training accompanied by their teachers.
The courses should be tailored to meet the requirement for various levels of competence and variety of skills.
LEVEL 1(Undergraduate) – Basic Surgical Skills, Basic Life Support Skills, Certifiable Procedural Skills, Normal Labour Management and Conduct of Delivery. These should be a mandatory part of clinical training of all undergraduates. Level 1 training facility is mandatory for all medical colleges.
As per National Medical Commission, the detailed Procedural skills for MBBS graduate are as follows:
A Comprehensive list of skills recommended as desirable for Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) – Indian Medical Graduate
| Specialty | Procedure |
| General Medicine |
• Venipuncture (I) • Intramuscular injection(I) • Intradermal injection (D) • Subcutaneous injection(I) • Intra Venous (IV) injection (I) • Setting up IV infusion and calculating drip rate (I) • Blood transfusion (O) • Urinary catheterization (D) • Basic life support (D) • Oxygen therapy (I) • Aerosol therapy / nebulization (I) • Ryle’s tube insertion (D) • Lumbar puncture (O) • Pleural and ascitic aspiration (O) • Cardiac resuscitation (D) • Peripheral blood smear interpretation (I) • Bedside urine analysis (D) |
| General Surgery |
• Basic suturing (I) • Basic wound care (I) • Basic bandaging (I) • Incision and drainage of superficial abscess (I) • Early management of trauma (I) and trauma life support (D) |
| Orthopaedics |
• Application of basic splints and slings (I) • Basic fracture and dislocation management (O) • Compression bandage (I) |
| Gynecology |
• Per Speculum (PS) and Per Vaginal (PV) examination (I) • Visual Inspection of Cervix with Acetic Acid (VIA) (O) • Pap Smear sample collection & interpretation (I) • Intra- Uterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD) insertion & removal (I) |
| Obstetrics |
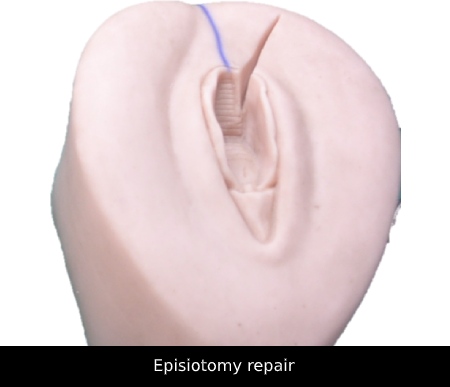
• Obstetric examination (I) • Episiotomy (I) • Normal labor and delivery (including partogram) (I) |
| Paediatrics |
• Neonatal resuscitation (D) • Setting up Pediatric IV infusion and calculating drip rate (I) • Setting up Pediatric Intraosseous line (O) |
| Forensic Medicine |
• Documentation and certification of trauma (I) • Diagnosis and certification of death (D) • Legal documentation related to emergency cases (D) • Certification of medical-legal cases e.g. Age estimation, sexual assault etc. (D) • Establishing communication in medico-legal cases with police, public health authorities, other concerned departments, etc (D) |
| Otorhinolaryngology |
• Anterior nasal packing (D) • Otoscopy (I) |
| Ophthalmology |
• Visual acuity testing (I) • Digital tonometry (D) • Indirect ophthalmoscopy (O) • Epilation (O) • Eye irrigation (I) • Instillation of eye medication (I) • Ocular bandaging (I) |
| Dermatology |
• Slit skin smear for leprosy (O) • Skin biopsy (O) • Gram’s stained smear interpretation(I) • KOH examination of scrapings for fungus (D) • Dark ground illumination (O) • Tissue smear (O) • Cautery – Chemical and electrical (O) |
|
I- Independently performed on patients, O- Observed in patients or on simulations, D- Demonstration on patients or simulations and performance under supervision in patients Certification of Skills: Any faculty member of concerned department can certify skills. For common procedures, the certifying faculty may be decided locally. |
|
LEVEL 2 (Postgraduate) – Advanced Life Support and Refresher Level 1 Courses, Basic Laparoscopic Skills Course, Neonatal and Paediatric Resuscitation Skills. Level 2 skills training centres are desired in each medical college; however if there are financial constraints, these could be conducted in collaboration with regional centres.
LEVEL 3 (Additional postgraduate) These will be available for multi-institutional use. Course will include Microsurgical Skills Courses, Advanced Laparoacopic Skills Courses and Human Patient Simulators for Anaesthesia, Pharmacology, Physiology and other physiology competencies. Level 3 is to be offered only in regional skill training centres and above, mainly because of its cost-effectiveness. Interns should have a mandatory Level I Certification before they get their Licensure degree.
Area Requirements for Skill Laboratory: 800 sq. m for 250 undergraduate annual intake institutions.
1. Four Rooms of 20 X 10 feet size for standardised patients. These rooms are for assessing communication skills, clinical signs demonstration, clinical examination of respiratory, cardiovascular, peripheral & central nervous systems, visual acuity testing, Digital tonometry, indirect ophthalmoscopy, eye irrigation, gastrointestinal & hepatobiliary system clinical examination. All these rooms are adequately ventilated, illuminated and have audio-video recording facility.
2. One room for demonstration of skills to small groups of 20 X 30 feet size
3. One area of 50 X 30 feet specifically for debriefing. This area/ hall contains AV equipment and video playback facility.
4. One room (10 X 10 feet size) for the Coordinator
5. One room ( 20 X 15 feet size) for the supporting staff of AV technician, maintenance technician and clerical staff
6. Storage space for the storage of mannequins and other equipment (of 30 X 20 feet size)
7. Specialty Rooms (of size 20 X 15 feet size) for Obstetrics, Gynaecology, Orthopaedics, ENT & Ophthalmology, Dermatology, and General Surgery). A total of 7 rooms with AV recording facility.
8. Another room of 30 X 20 size for General Medicine.
9. The list of equipment in these rooms are described as below.
Educational Content
All simulation content stations are having aligned goals and objectives. Each station will be having predefined learning objectives. Simulation objectives shall include cognitive, affective ad psychomotor domains. Simulation scenarios are validated and standardized for effective competence assessment. Simulation scenarios are also integrated into the prescribed curriculum. Assessment of students using OSCE or minicex assessment scores for comparability are available. At the end of training session, debriefing session will be organised to support or modify the training procedure carried out by the student.
Trained Faculty:
The key to a successful skills and simulation training centre is the availability faculty and the avenues for continuous faculty development. The core simulation staff is designated and received appropriate training at the University approved centre. These trained faculty are in turn facilitating incorporation of simulation into existing curriculum and running training sessions. A real time schedule for training of additional faculty is in existence. There are facilities for periodical assessment of the trained faculty.
Trained Faculty:
1. Dr Raghu. Clinical Services consultant, Department of Emergency Medicine
2. Dr Gopala Krishna, Assistant Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine
3. Dr Ravishankar, Assistant Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine
4. Dr U Gangaram, Associate Professor of Internal Medicine
5. Dr Susheel, Assistant Professor, Department of Hospital Administration
6. Dr Ajay Reginald, Principal, Narayana Dental College
7. Dr Sridhar, Professor of Oral-maxillofacial Surgery
8. Dr Rakesh, Assistant Professor, Department of PM & R
9. Dr Ravi Raj, Assistant Professor, Department of PM & R
10. Dr K Vaishnavi, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine
11. Dr Vishnu Vandana, Associate Professor, Department of Paediatrics
12. Ms. K Subhasini, Department of Nursing
13. Ms. M Naseema, Department of Nursing
14. Mr. S Sateesh, Emergency Medicine Technician
15. Mr. Siva Krishna, Anaesthesia Technician
Sample Floor Plan:
The skill laboratory is situated at the Ground floor of the administrative building of Narayana medical College. The floor plan consists of
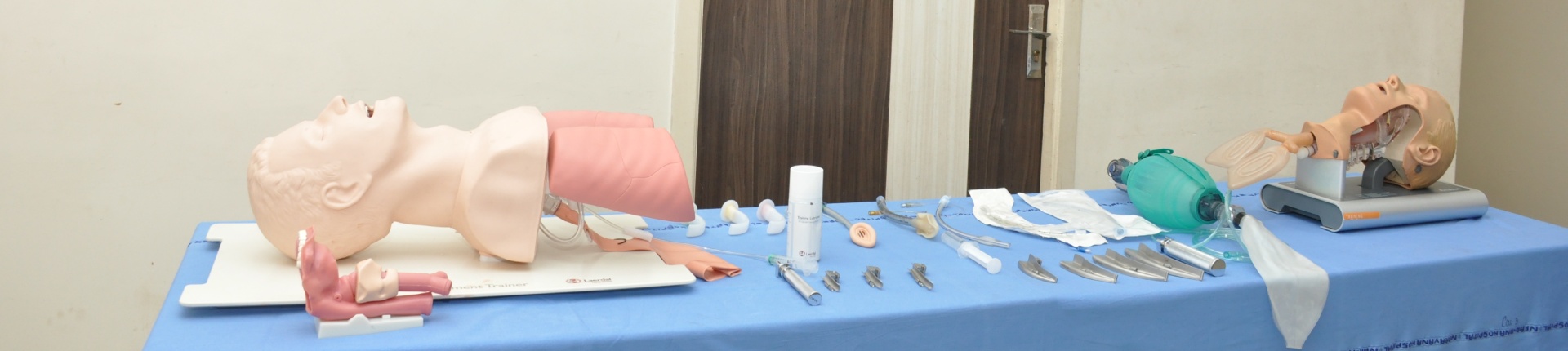
Simulators
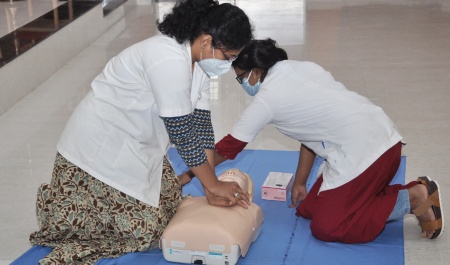
Little Anne CPR Manikin
This mannequin has been developed to provide effective adult CPR training without compromising realism or quality. Its durable and convenient design makes hands-on practice affordable for every student. It has a mechanical indicator showing the amount of pressure individual is exerting over the sternum while applying CPR technique. The green and red coloured zones indicate the correct and incorrect ways of doing.
• Through these mannequins, students will be able to learn and practice oral and nasal passages allowing realistic nose pinch required for mouth-to-nose ventilation
• Natural obstruction of the airway allows students to learn the important technique of opening the airway
• Head tilt/chin lift and jaw thrust allow students to correctly practice all manoeuvres necessary when resuscitating a real victim
• Realistic airway function means that the airway remains obstructed without proper head tilt/chin lift or jaw thrust. Chest rise is seen with correct ventilations
• Anatomically correct landmarks and sternal notch allow the student to practice identification of all anatomical landmarks relevant to adult CPR
• Audible feedback reinforces correct compression depth. A “clicker” feature signals the correct compression depth
• Realistic chest compression resistance allows the students to experience the amount of pressure needed to perform proper chest compressions in a real-life situation
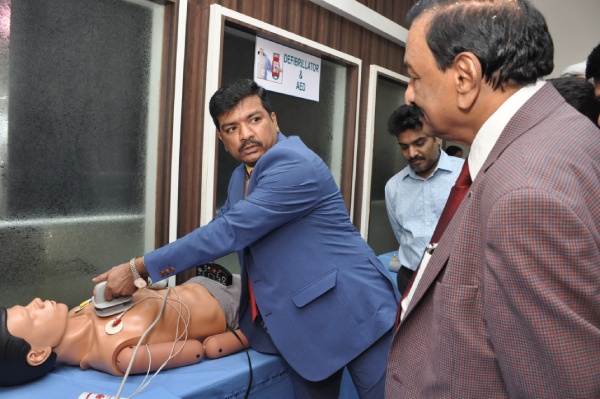
Defibrillator Mannequin:
These mannequins are capable of imitating 17 rhythms and pacing. They can be programmed for the upper teeth breakout and tongue edema and cricothyrotomy. There are bilateral chest decompression sites and bilateral chest tube insertion sites. There are 12 pulse point to detect decrease in the blood pressure and pulse volume. There is also facility for phlebotomy. Once defibrillated, the mannequin will be able to show the automatic return of carotid pulse. This mannequin is also fitted with interactive ECG simulator.
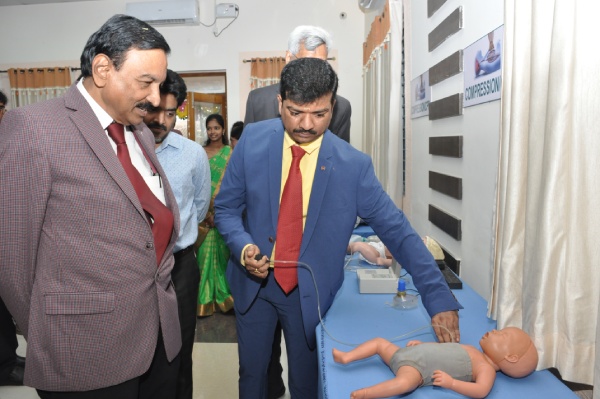
Dr P Syama prasad, Vice Chancellor, NTR University of Health Sciences appreciating the learning experience with Defibrillator mannequin.
Choking Mannequin:
This mannequin of adult torso designed specifically for training students in the performance of the Heimlich Abdominal Thrust Maneuver. Students can
practice the Five and Five approach on this mannequin. The assessment of learning can be carried out through OSCE.
Dr Satish, Medical Superintendent in-charge is demonstrating the method of management of choking in young children
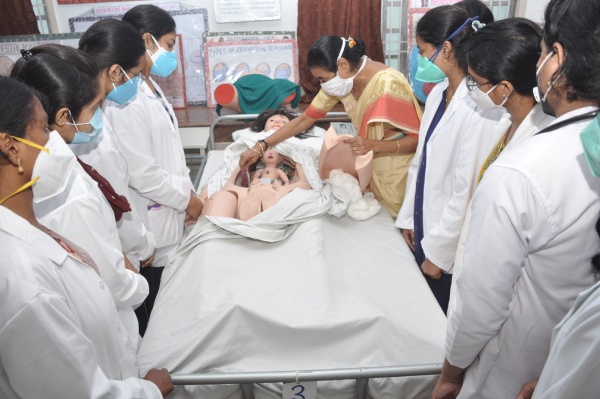
SimMom and MamaBirthie
SimMom and MamaBirthie combined provide an impactful simulation toolkit, which can be used at different stages of the Circle of Learning to support a complete learning experience.
One of the most important objectives during labor and delivery is recognizing the potential risks to both the mother and baby. By building a well-trained team, confident in their abilities to manage adverse events whilst communicating with respect to the mother, you ensure better outcomes for both patients. Students can repeatedly practice the delivery technique on this mannequin. It allows the students to get hands-on experience with standard procedures like
• fundal grips
• Vaginal and abdominal examinations
• Use the cervical inserts for dilatation and effacement assessment, as well as identifying positioning
• Palpate the baby’s position using anatomical landmarks
• Effectively learn complex birth procedures such as vacuum-assisted delivery, breech and shoulder dystocia
• Gain tactile feedback from BabyBirthie’s palpable fontanelles
Students practice the procedures and faculty supervise these skills. Students are apt to commit mistakes during these procedures. Faculty trained with this obstetric solution, teams can train for decision-making in emergency settings and the ability to work under pressure in a safe environment.
With immediate feedback from either simulator or role-play, trained faculty can pinpoint areas of improvement, teach precise behaviours for real-life emergency procedures, and instil confidence over time. Narayana Medical College is practicing the Hybrid simulation which can improve patient outcomes and patient satisfaction, as it combines skills assessment in both clinical treatment and communication with a standardized patient.
Students can appreciate that this mannequin is ideal for practicing interaction and active listening in role-play settings. By using it for peer-to-peer training sessions, students build engagement for respectful care, effective communication, and risk managing.
This obstetric solution enables training on both standard deliveries and life-threatening emergencies. The position of the foetus can be programmed for vertex or breech and can also be designed for prolapse. By utilizing best-practice methodologies in simulation, students can prepare for low-frequency, high-risk emergencies. This would confidently enhance students’ psychomotor skills and promote the best possible patient care.
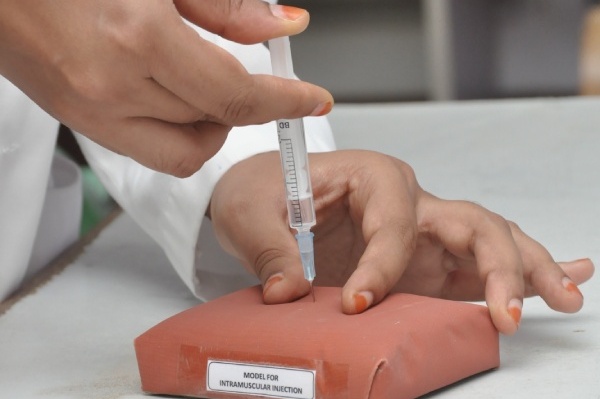
Injection Techniques:
The indigenously developed soft tissue injection pad is designed by students and faculty of Narayana Medical College for practising intradermal, subcutaneous and intramuscular tissue injection techniques. The model Trainer has multiple tissue layers representing the epidermis, dermis, fat and muscle layer, and can easily attach to an arm or thigh to help teach professional-to-patient communication.
Learning the technique of Intramuscular injection
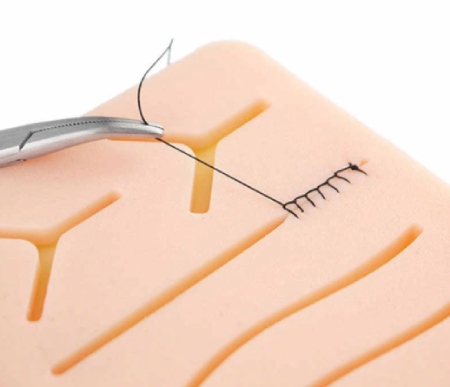
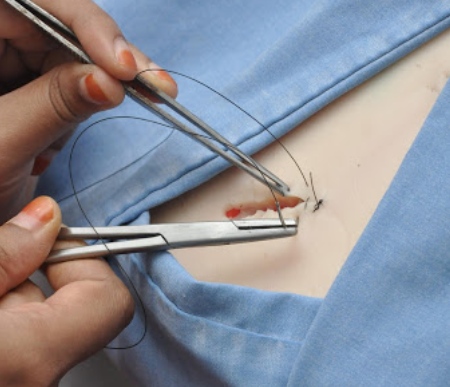
Suturing Techniques:
Students are exposed to the Plastiskin models to learn the technique suturing. The Faculty and students of Narayana Medical College also developed indigenous models for learning suturing techniques.
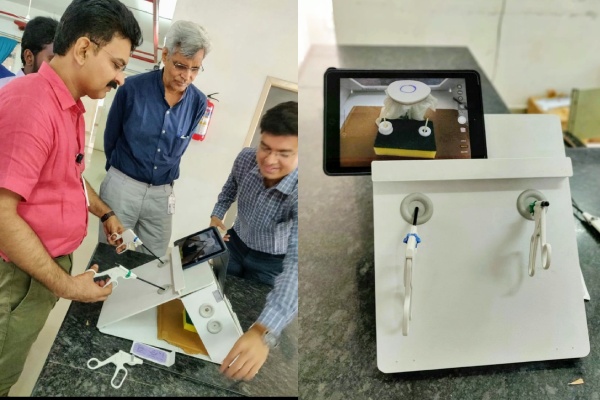
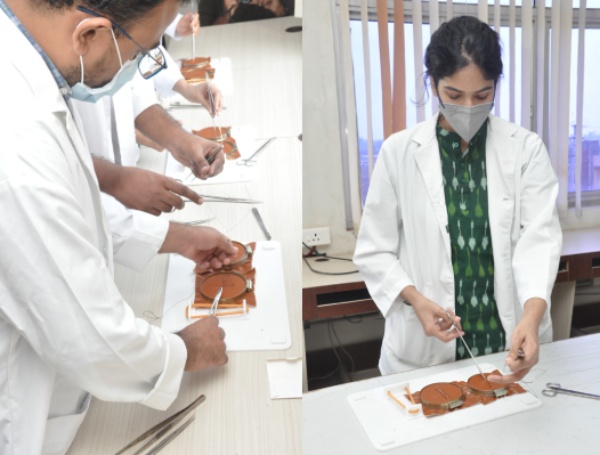
Laparoscopy Techniques:
Postgraduate students of surgical disciplines are exposed to learn the techniques of laparoscopy through indigenously developed models and mannequins. The laparoscopy is attached with a visualisation monitor wherein students can observe the movement of the laparoscope and can practice the skill. Through this mannequin, students learn to practice excision, suturing and other skills associated with laparoscopy.
Simulation Centre
A learning management resource for healthcare simulation and education
Simulation centre allows medical students to effectively manage, record, and assess simulation training, both on-site and in-situ. Capture audio, video, annotations, patient monitors, and simulator data. Once replayed, the student is debriefed about the performance and suggested methods for improvement.
The simulation centre is effective to deliver high-quality clinical training, medical education, and quality improvement in clinical skills.


 CINEC
CINEC